Headless commerce has revolutionized how ecommerce businesses deliver personalized fast and seamless customer experiences. Shopify Headless allows developers to decouple the frontend from Shopify’s backend, giving full control over presentation, interactivity, and performance.
At the heart of efficient Shopify Headless development is GraphQL, a powerful API query language that provides fast, flexible, and structured access to Shopify store data. By leveraging GraphQL developers can fetch exactly the data they need, reduce payload size, and simplify integration between Shopify and modern front-end frameworks such as React Next.js or Hydrogen.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of using GraphQL for Shopify Headless development including benefits, setup, querying strategies, best practices, common challenges, and advanced tips for developers.
I. Why Use GraphQL for Shopify Headless
GraphQL is an alternative to traditional REST APIs that allows developers to query multiple resources in a single request. When paired with Shopify Headless, it provides several advantages:
- Efficiency: Retrieve exactly the fields you need in one query, minimizing data transfer and load time
- Flexibility: Fetch multiple related resources in a single request (e.g., products, collections, and inventory)
- Strong Typing: GraphQL schemas provide clear definitions, reducing errors and improving maintainability
- Developer Productivity: Auto-generated documentation and introspection simplify API usage
- Real-Time Capabilities: Subscriptions and webhooks allow live updates without polling
Using GraphQL ensures that Shopify Headless storefronts can deliver high-performance user experiences, even under heavy traffic or with complex data structures.
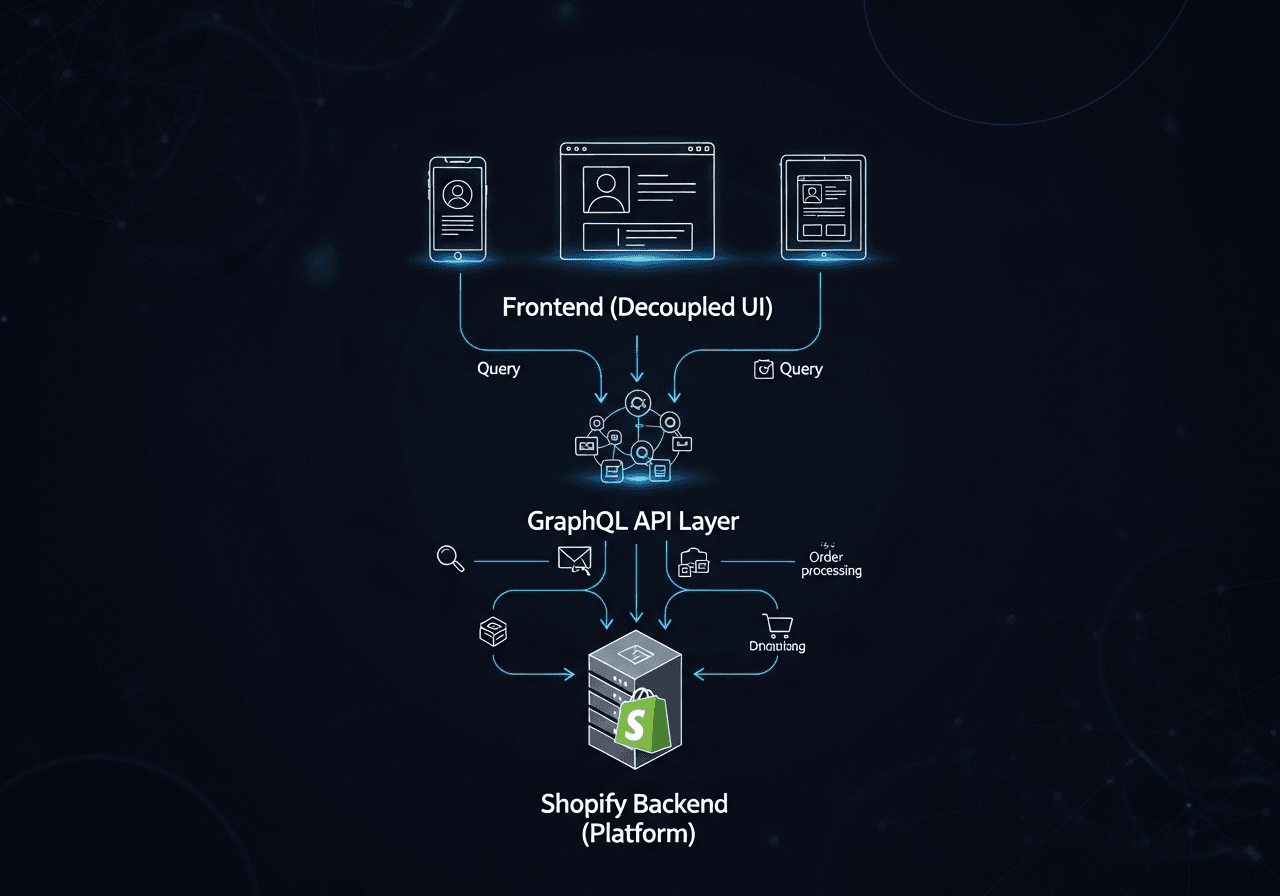
II. Understanding Shopify Headless Architecture
Before diving into GraphQL, it is essential to understand Shopify Headless architecture:
- Shopify Backend: Handles product catalog, inventory, checkout, and order management
- Headless Frontend: Built with modern frameworks like React, Next.js, Vue, or Hydrogen, decoupled from Shopify’s liquid templates
- GraphQL API Layer: Facilitates communication between frontend and Shopify backend
- Optional Middleware: Can aggregate data from multiple sources such as CMS, personalization engines, or third-party services
This separation of frontend and backend allows developers to implement customized experiences without being constrained by Shopify’s standard themes.
III. GraphQL Basics for Shopify Developers
GraphQL uses a schema to define types and queries. Key elements include:
-
Query: Request data from the API
-
Mutation: Modify or add data
-
Subscription: Listen to real-time updates
-
Schema: Defines types, fields, and relationships
In Shopify, the Storefront API exposes GraphQL endpoints for querying:
-
Products: Title, description, images, variants
-
Collections: Group products for thematic presentation
-
Customers: Accounts, orders, and addresses
-
Checkouts: Cart creation, line items, and payment processing
Unlike REST APIs, which may require multiple requests to gather related resources, GraphQL queries return all necessary data in a single response.
IV. Setting Up GraphQL for Shopify Headless
1. Create a Shopify Storefront API Access Token
- Log in to Shopify admin
- Go to Apps > Manage private apps > Create new app
- Assign Storefront API permissions (read_products, read_collections, etc.)
- Generate an API token
2. Choose a Frontend Framework
Popular frameworks for Shopify Headless development:
- React with Next.js: Server-side rendering, SEO-friendly
- Hydrogen: Shopify’s React framework optimized for Storefront API
- Vue/Nuxt: Alternative with flexible SPA architecture
3. Install GraphQL Client
- Apollo Client: Widely used with React
- Relay: Optimized for large GraphQL apps
- urql: Lightweight, easy to configure
4. Configure Environment Variables
Store API keys and Shopify domain in environment variables to protect sensitive data.
5. Test Queries
Use tools like GraphiQL or Insomnia to experiment with GraphQL queries before integrating them into your frontend code.
V. Example Shopify GraphQL Queries
Querying Products
query {
products(first: 10) {
edges {
node {
id
title
description
images(first: 3) {
edges {
node {
url
}
}
}
variants(first: 5) {
edges {
node {
id
title
priceV2 {
amount
currencyCode
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
This query retrieves the first 10 products along with images and variants in a single request.
Creating a Checkout
mutation {
checkoutCreate(input: {
lineItems: [
{ variantId: "gid://shopify/ProductVariant/12345", quantity: 1 }
]
}) {
checkout {
id
webUrl
}
}
}
This mutation creates a checkout session for the customer.
Fetching Collections
query {
collections(first: 5) {
edges {
node {
title
description
products(first: 3) {
edges {
node {
title
priceRange {
maxVariantPrice {
amount
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Retrieve multiple collections along with top products efficiently.
VI. Best Practices for GraphQL in Shopify Headless
- Use Fragments for Reusability: Define common query fragments to avoid duplication
- Paginate Requests: Avoid fetching excessive data in a single query
- Leverage Caching: Use Apollo or CDN caching to reduce API calls
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling for API failures
- Monitor Performance: Log slow queries and optimize schema usage
- Use Environment-Specific Endpoints: Separate development, staging, and production
VII. Advanced GraphQL Techniques
1. Real-Time Updates with Subscriptions
-
Listen for inventory or price changes
-
Trigger frontend updates without polling
2. Dynamic Content with CMS Integration
-
Combine Shopify GraphQL queries with headless CMS (Sanity, Contentful, Strapi) for content-rich experiences
-
Example: Query products from Shopify and fetch editorial content from CMS in a single frontend view
3. Server-Side Rendering
- Use Next.js or Hydrogen SSR to prefetch GraphQL data for SEO
- Reduce time-to-first-byte and improve page load
4. Combining Multiple APIs
- Fetch Shopify data alongside third-party APIs like recommendation engines or personalization services
- Aggregate results using a serverless function or Node.js backend
IV. Common Challenges and Solutions
V. Performance Tips
-
Optimize Queries: Avoid fetching unused fields
-
Implement Lazy Loading: Load product images and heavy data only when needed
-
Use CDN for Static Assets: Serve images and media efficiently
-
Monitor API Limits: Shopify imposes query cost limits; plan queries accordingly
-
Batch Requests: Combine multiple small queries into one when possible
VI. Case Study Example
A mid-sized ecommerce brand migrated to Shopify Headless using Next.js and GraphQL. Key improvements:
- Reduced page load time by 40%
- Simplified frontend data handling with single GraphQL queries
- Enabled personalized content across multiple channels
- Reduced API calls by 30% using caching and fragments
The GraphQL approach allowed them to scale seamlessly and deliver a modern, interactive storefront without performance bottlenecks.
VII. How to Start Using GraphQL with Shopify Headless
- Set up a Shopify store and enable Storefront API
- Choose your frontend framework (React, Hydrogen, Vue)
- Install a GraphQL client like Apollo
- Test your queries using GraphiQL or similar tools
- Fetch products, collections, and checkout data efficiently
- Integrate with headless CMS for content-rich storefronts
- Implement caching, pagination, and error handling for production
Conclusion
GraphQL is a cornerstone for modern Shopify Headless development. Its ability to deliver precise, flexible, and efficient queries allows developers to build high-performance, scalable storefronts that meet the demands of today’s ecommerce landscape.
By mastering Shopify Headless GraphQL, developers gain the ability to fetch data efficiently, significantly reducing frontend load and improving performance. They can seamlessly combine multiple data sources, including headless CMS platforms and third-party APIs, to create cohesive and dynamic storefront experiences. This approach enables the development of fast, SEO-friendly, and highly interactive user interfaces, enhancing engagement and conversions. Moreover, leveraging GraphQL allows teams to scale their ecommerce architecture effectively, supporting enterprise-level operations with robust performance and flexibility.
Read more:
